Virtual Clusters
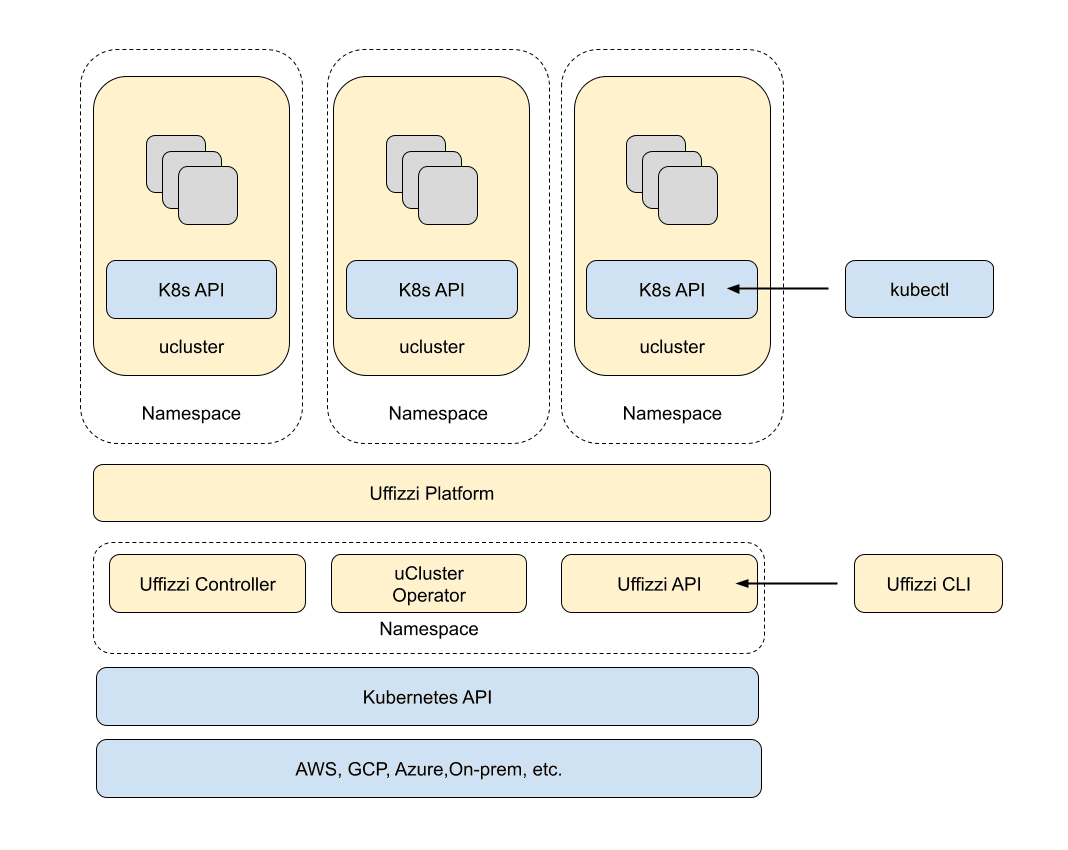
Similar to the concept of virtual machines, Uffizzi virtual clusters are virtualized instances of Kubernetes clusters running on top of a host cluster. Uffizzi virtual clusters provide all the same functionality of real Kubernetes clusters, while being more convenient and efficient.
Inside each virtual cluster is a full copy of the Kubernetes API—i.e. each developer can query his or her own instance of the K8s control plane. This means Uffizzi virtual clusters can safely support custom resource definitions (CRD) and other components that require cluster-wide access.
You can create virtual clusters from the Uffizzi CLI, then apply Helm charts, kustomizations, or regular Kubernetes manifests. Once created, you can manage Uffizzi virtual clusters with kubectl.
Example Usage
$ uffizzi cluster create my-cluster
# Creating cluster my-cluster...
$ kubectl apply -f ./manifestsArchitecture
Uffizzi works by virtualizing the Kubernetes control plane (i.e. the entire K8s API). It creates a namespace for every virtual cluster, then deploys a full installation of Kubernetes within the namespace.
Uffizzi handles user management, enforces fair sharing of resources among tenants, enforces network policies, and more. You can read more about resource sharing and the Uffizzi security model here:
- Kubernetes Virtual Clusters for Efficient Resource Utilization (opens in a new tab)
- Secure Multi-tenant Kubernetes with Virtual Clusters (opens in a new tab)
Kubernetes API Versions
Several Kubernetes API versions are supported by Uffizzi virtual clusters, including 1.28, 1.27, 1.26, and 1.25.
You can specify which version of the Kubernetes API to use when creating the cluster, either in the UI, or from the Uffizzi CLI by passing the --k8s-version=<version> flag.
Minor versions point to the latest patch release of the corresponding k3s minor version. See https://github.com/k3s-io/k3s/releases (opens in a new tab) for the latest patches.
Benefits
Easy provisioning - Using the Uffizzi CLI, you can create a cluster and update your kubeconfig in a single command, then use standard Kubernetes tools like kubectl to manage the cluster. Once you're done, clean everything up with a simple uffizzi cluster delete command.
Bring your own tools - Uffizzi virtual clusters work with the most popular Kubernetes management tools including kubectl and helm.
Increased productivity - With Uffizzi virtual clusters, developers no longer have to wait on cluster availability for testing, and if your team is self-hosting Uffizzi, operations teams only need to manage a single host cluster.
Secure scaling - Uffizzi virtual clusters provide secure multi-tenant Kubernetes out of the box, so workloads can safely and efficiently share underlying compute resources. This means every developer on your team can test their code in dedicated and isolated clusters whenever they need them.
Cost-effective testing - Whether you install Uffizzi on your own host cluster or are relying on Uffizzi Cloud, virtualization is the most cost-effective way to power your Kubernetes-based test environments.
Getting started
- To get started with Uffizzi virtual clusters, follow the quickstart guide.
- To get started testing against different version of the Kubernetes API, see this guide.