GitHub Actions Virtual Cluster Example
Follow the example guide below to see how the Uffizzi virtual cluster integration with GitHub Actions works end-to-end. Or you can skip ahead to the recipe if you'd rather get started integrating Uffizzi with your project.
Get Started
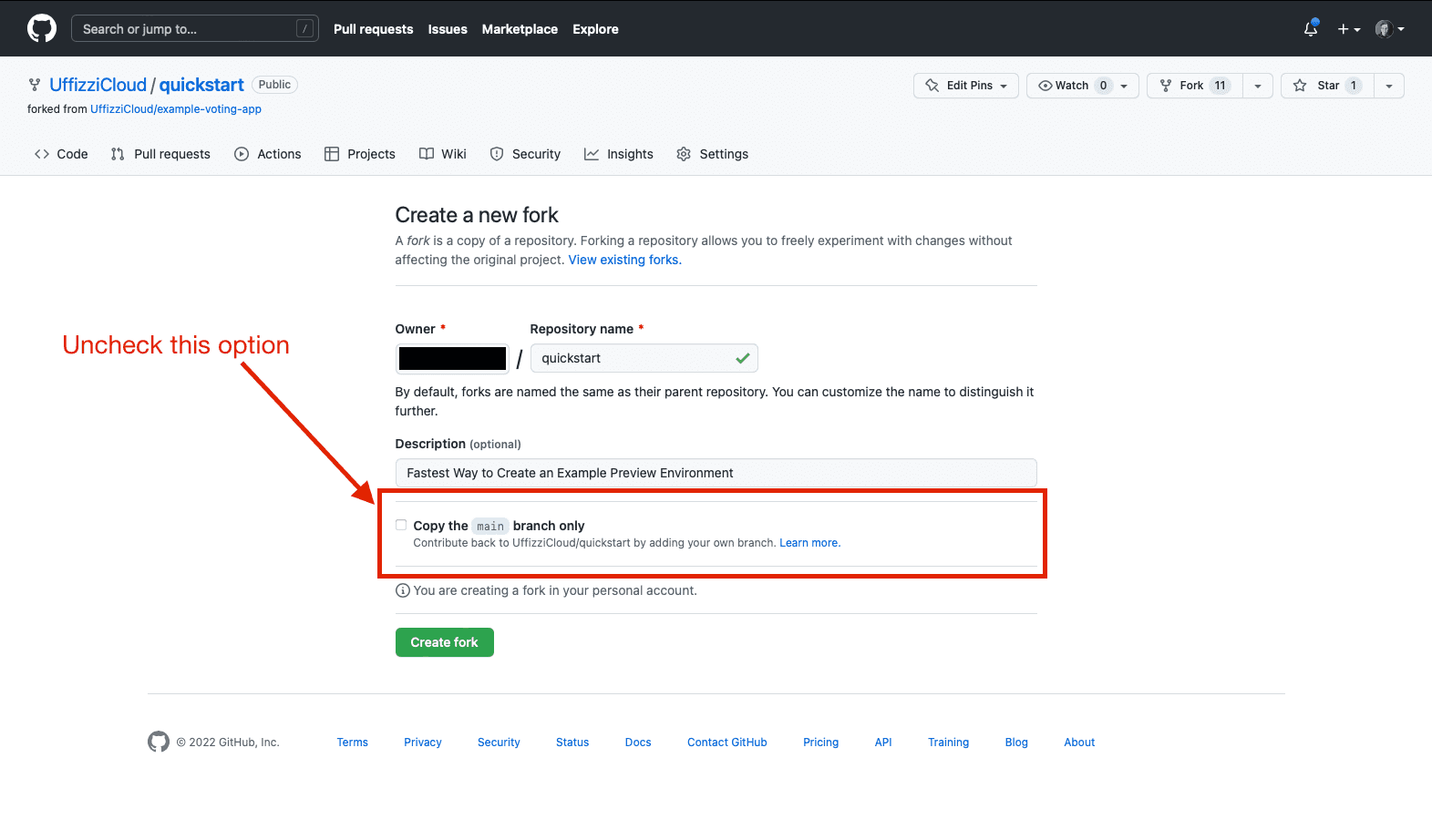
Fork the quickstart repo
Start by forking the quickstart (opens in a new tab) repository on GitHub, if you haven't already.
Be sure to uncheck the option Copy the main branch only. This ensures that the try-uffizzi branch will be included in your fork.
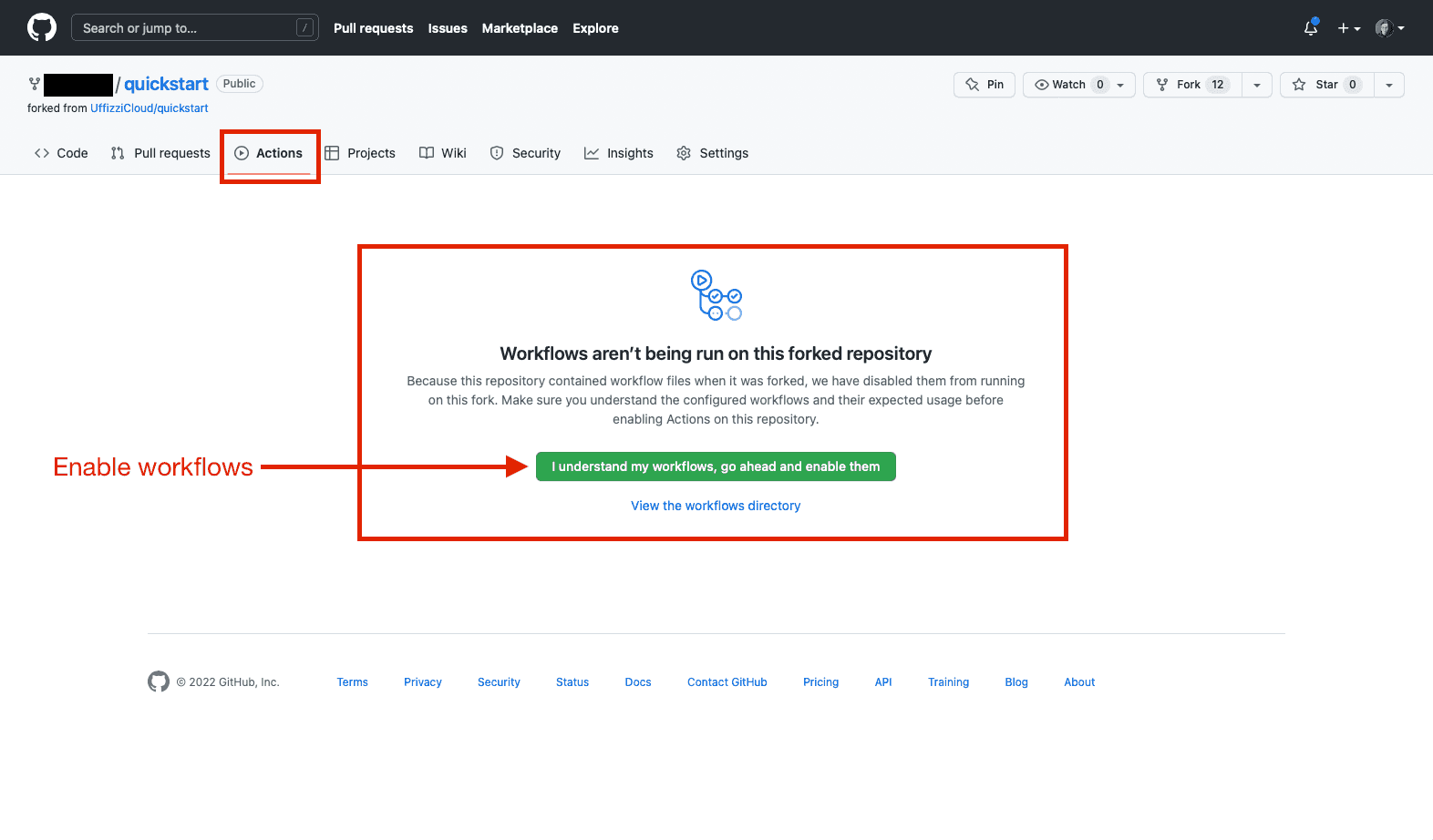
Enable GitHub Actions workflows
Enable GitHub Actions workflows for your fork by selecting Actions, then select I understand my workflows, go ahead and enable them.
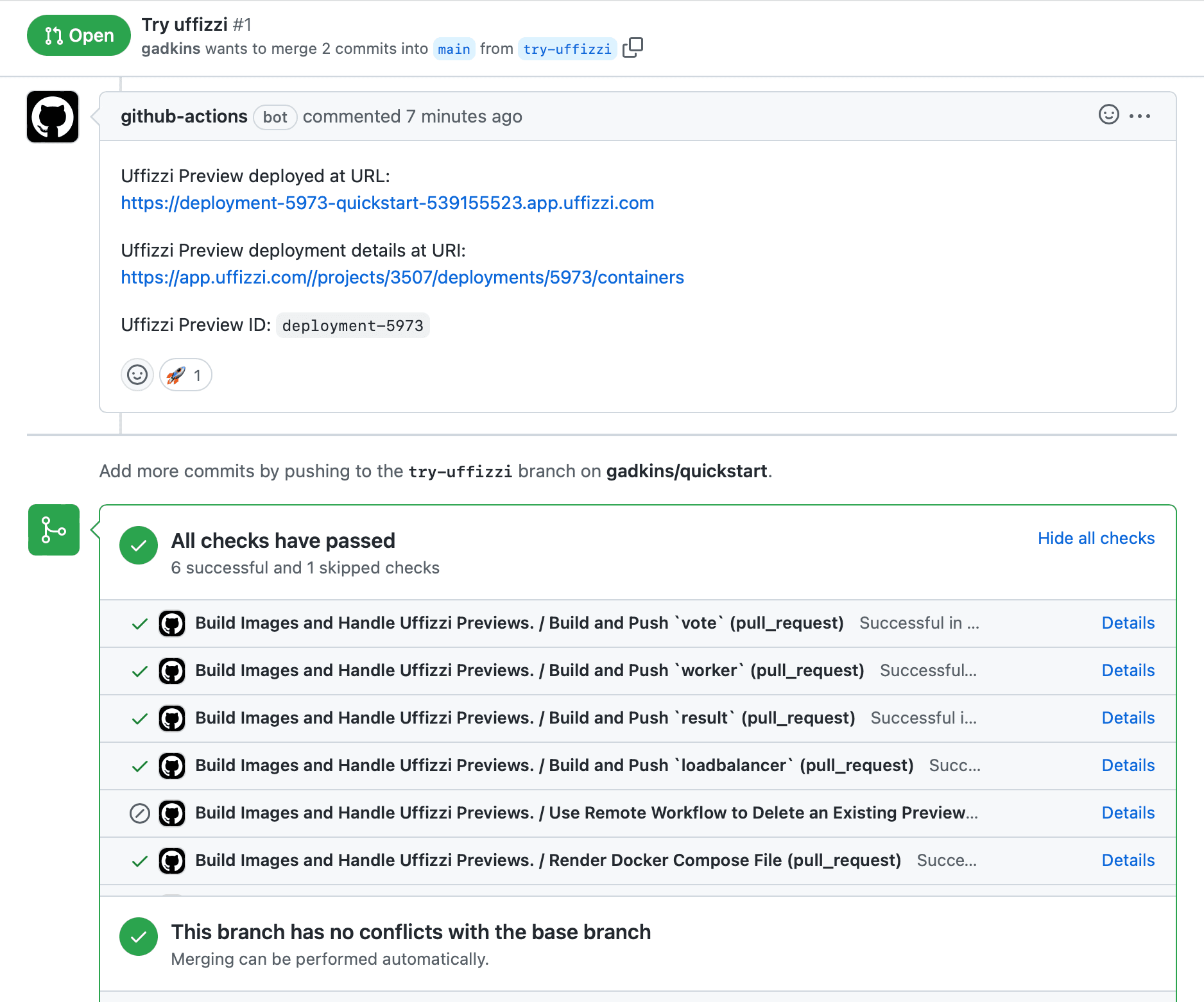
Open a PR
Open a pull request for try-uffizzi branch against main in your fork.
Be sure that you're opening a PR on the branches of your fork (i.e. your-account/main ← your-account/try-uffizzi). If you try to open a PR for UffizziCloud/main ← your-account/try-uffizzi, the Actions workflow will not run in this example.
What to expect
The PR will trigger a GitHub Actions workflow (opens in a new tab) that uses the Uffizzi CLI and Kubernetes manifests to create a Uffizzi ephemeral environment for the microservices application defined by the repo. When the workflow completes, the ephemeral environment URL will be posted as a comment in your PR issue.
This virtual cluster is configured with a Uffizzi Ingress, which makes the web service available at a predictable URL, consisting of https://app.uffizzi.com/ appended with the GitHub pull request domain. For example:
https://app.uffizzi.com/github.com/{account}/{repo}/pull/{pull-request-number}.
You can make requests to specific endpoints by appending a route to the end of the URL. For example:
https://app.uffizzi.com/github.com/boxyhq/jackson/pull/661/api/health
To learn how to enable predicable URLs for your ephemeral environments, see the [Uffizzi Ingress(/docs/ingress) documentation].
How it works
Ephemeral environments are configured with a Kubernetes manifest (opens in a new tab) that describes the application components and a GitHub Actions workflow (opens in a new tab) that includes a series of jobs triggered by pull_request events.
When a pull request is open/closed/reopened/updated, the workflow will run the following jobs:
- Build and Push the Image
- Create a virtual cluster using the Uffizzi CLI in a GitHub Actions runner
- Apply a kustomization to deploy the application on the virtual cluster
- Post a new comment or update an existing comment with the ephemeral environment URL and instructions for accessing the environment
- Delete the virtual cluster when the PR is closed or merged
Connecting to the Cluster
To run kubectl commands on this cluster, first update your kubeconfig by running:
uffizzi cluster update-kubeconfig [CLUSTER_NAME]Tip: We recommend using the pull request number for cluster names to make it easy to connect to your clusters, e.g.: uffizzi cluster update-kubeconfig pr-281
To find the ingress of this deployment, run:
kubectl get ingress web --kubeconfig ~/.kube/config -o json | jq '.spec.rules[0].host' | tr -d '"'Next Steps
Now that you've seen the process from start to finish, add Uffizzi to your own project on GitHub.